In the world of veganism, not all food additives are created equal. As plant-based diets continue to gain popularity, it’s crucial for vegans to navigate the complex landscape of food additives. These substances, added to enhance flavor, texture, and shelf life, can be a minefield for those committed to an animal-free lifestyle. Let’s dive into the world of vegan-friendly (and not-so-friendly) food additives.
The Role of Additives in Vegan Products
Food additives are the unsung heroes of the vegan food industry, playing a vital role in creating plant-based alternatives that rival their animal-derived counterparts. They help improve taste, texture, and appearance while extending shelf life. However, not all additives align with vegan principles.
Vegan-Friendly vs. Animal-Derived Additives
To be considered vegan-friendly, additives must be of vegetable or mineral origin and free from animal-derived ingredients. Common animal-derived additives to watch out for include:
- Riboflavin (E101 or E106): Often sourced from dairy, eggs, or liver
- Cochineal/Carmine (E120): A red dye derived from insects
- Gelatin (E441): Extracted from animal tissues
- Beeswax (E901): Produced by bees
- Lanolin (E913): Derived from sheep’s wool

The Grey Area: Additives of Ambiguous Origin
Some additives can be derived from either plant or animal sources, making them tricky to navigate. These include:
- Glycerol (E422): Used as a humectant and sweetener
- Mono and diglycerides of fatty acids (E471): Common emulsifiers
- Lecithin (E322): Can be sourced from soy or eggs
When encountering these additives, it’s essential to investigate further or look for vegan certifications.
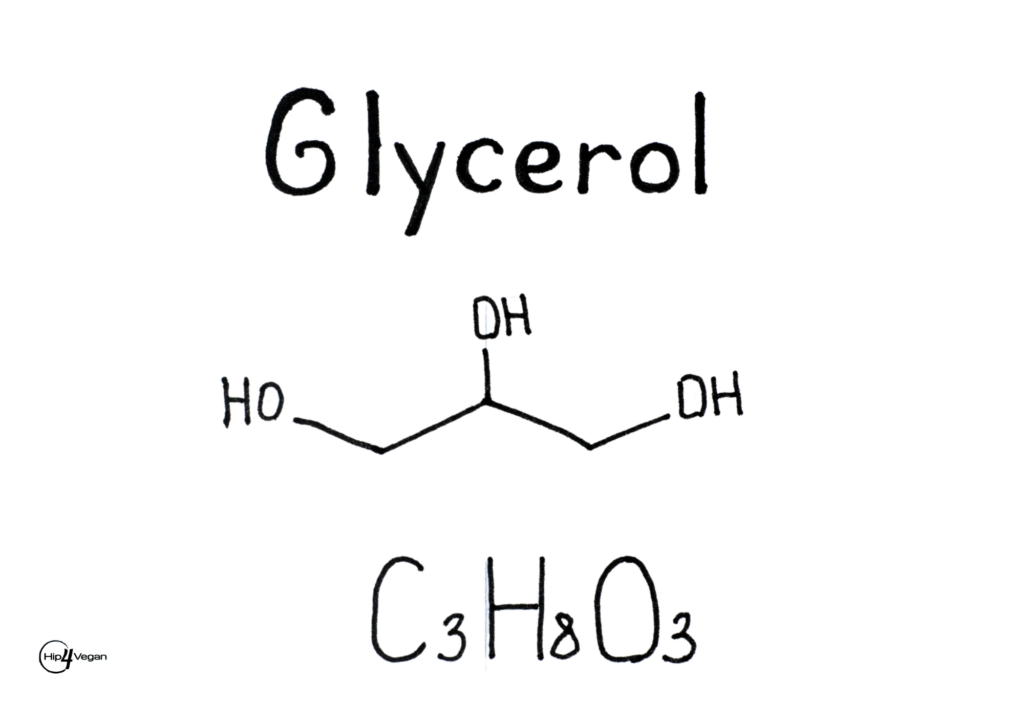
Deciphering Labels and Certifications
Reading product labels carefully is crucial for maintaining a vegan diet. Look out for:
- Ingredient lists: Identify potentially problematic additives
- Alternative names: Be aware of different terms for animal-derived additives
- Vegan certifications: These can provide assurance of a product’s vegan status
Vegan Alternatives to Common Animal-Derived Additives
The food industry has developed numerous plant-based alternatives to replace animal-derived additives:
- Agar-agar as a substitute for gelatin in desserts
- Soy lecithin instead of egg-derived lecithin
- Plant-based dyes like chlorophyll to replace carmine

Maintaining a Healthy and Ethical Vegan Diet
To ensure a balanced and ethical vegan diet while navigating food additives:
- Develop a well-rounded meal plan that meets nutritional needs
- Choose whole, minimally processed foods when possible
- Support brands committed to ethical and sustainable vegan food production
- Stay informed about common additives and their sources
The Bigger Picture
Choosing vegan-friendly additives goes beyond personal health—it’s a commitment to animal welfare and environmental sustainability. By being mindful of the additives in our food, we can make more informed choices that align with vegan principles.
In conclusion, while navigating food additives as a vegan can seem daunting, it becomes easier with knowledge and practice. By understanding common additives, reading labels carefully, and choosing certified vegan products, we can maintain a diet that’s not only healthy but also consistent with our ethical beliefs. Remember, every mindful choice contributes to a more compassionate and sustainable food system.